In today’s world, dietary preferences and sensitivities are increasingly in the spotlight. Gluten intolerance and Celiac have emerged as common and often misunderstood conditions. For those who deal with gluten sensitivity, they know that with gluten intolerance comes more than just mild discomfort. There are a massive array of symptoms that can arise from gluten consumption that disrupt the flow of everyday life. One of the most pervasive and distressing symptoms associated with gluten intolerance is gluten diarrhea. In this article we will address the relationship between gluten and diarrhea and offer guidance on how to manage this relationship for a healthier, more comfortable lifestyle.
What is gluten?
Gluten is the protein in grains that lends elasticity to bread and other baked goods. Gluten is often associated with wheat, rye, and barley. However, we know that gluten protein can be found in
ALL grains. Common foods containing gluten include pasta, bread, baked goods, and
beer, as well as many sauces, condiments, and marinades.
For those with celiac disease, gluten can be incredibly harmful. Gluten can trigger an immune reaction causing inflammation in the intestines, which can result in a host of other health issues.
What is gluten sensitivity?
There are many people who have tested negative for celiac disease but experience symptoms from the ingestion of gluten or face a number of health issues including autoimmune diseases. These people are believed to have non celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS), a condition that has been suggested to affect
up to 6% of the United States population.
Although commonly thought to be less of a problem than celiac, NCGS can trigger immune reactions that in some cases are just as troubling. For an in depth breakdown on the differences between celiac disease and NCGS, watch our free
Glutenology© Masterclass here.
Symptoms of Gluten Exposure
The
symptoms of gluten exposure for those with celiac disease and gluten sensitivity can vary greatly from person to person which can make it challenging to identify gluten as the root cause. In addition, symptoms extend far beyond the digestive concerns that are most commonly discussed with respect to celiac disease and gluten sensitivity. Common symptoms include the following:
- Digestive symptoms such as bloating, gas, diarrhea, or constipation
- Skin issues like rash, eczema, or dermatitis herpetiformis
- Fatigue, brain fog, or difficulty concentrating
- Joint pain, muscle aches, or inflammation
- Headaches or migraines
- Mood changes, depression, or anxiety
- Nutrient deficiencies due to malabsorption
- Irregular menstrual cycles or fertility issues
Can gluten cause Diarrhea?
Gluten can contribute to intestinal inflammation in those who are sensitive. This can manifest in a number of different ways, including diarrhea. This section explains the ways in which gluten can cause diarrhea and how a gluten free diet can help resolve diarrhea.
Gluten-induced nutritional deficiencies
Gluten consumption can contribute to nutritional deficiencies. This is because many nutrients are absorbed in the small intestine, and when the intestines are damaged, they are unable to properly absorb nutrients. One common deficiency in those with celiac disease and gluten sensitivity is vitamin B12. A vitamin B12 deficiency can contribute to many symptoms, including
diarrhea. Other examples include deficiencies of vitamin B1, B3,
zinc, vitamin A, and vitamin D.
Bacterial and fungal overgrowths
Gluten induced immune responses can increase the risk of intestinal bacterial and fungal overgrowths that might contribute to diarrhea. In fact, some
research suggests that there is a correlation between celiac disease and candida overgrowth. In addition,
research suggests that some patients with celiac disease and small intestine bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) do not respond to traditional methods of treating SIBO.
Resolution of diarrhea with a gluten free diet
One study found that patients have substantial and rapid improvement of diarrhea symptoms upon the adoption of a gluten-free diet,
Another study found that a gluten free diet is effective in the long-term treatment of patients with previously unexplained chronic watery diarrhea or bloating. And
more research even suggested using the antigliadin IgG as a biomarker to identify patients with
irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) who might have reductions in diarrhea on a gluten free diet.
Dangers of diarrhea
Diarrhea means having a loose, watery stool during a bowel movement. Occasional or minor diarrhea is generally not a concern, but persistent, chronic, or severe diarrhea can come with some risks.
The biggest risk of diarrhea is dehydration. This can happen as the body is losing a lot of fluid through stools. Typically stools spend enough time in the large intestine that fluid gets absorbed by the body. But with diarrhea, stools pass through quickly and take fluid with them as they exit the body. Without treatment, dehydration can lead to kidney failure, stroke, heart attack or in the most severe and rare cases, even death.
Another risk of
persistent diarrhea is malnutrition. Excessive diarrhea can lead to malabsorption of fats, proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals in the diet.
In addition, a big risk of chronic or persistent diarrhea is not identifying the root cause of the diarrhea. Oftentimes, there is an underlying condition that causes chronic diarrhea. Left untreated, many conditions come with their own risks. Some such
conditions include celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, colitis, and pancreatitis.
Managing gluten diarrhea
The first step to manage gluten diarrhea is to
eliminate gluten from your diet, including
hidden forms of gluten. Next, ensure that you are hydrating well in order to restore some of the fluids lost through diarrhea.
Even after eliminating gluten from your diet, there is healing that must occur “behind the scenes”. This healing will address the intestinal damage from gluten consumption, plus the downstream effects of intestinal damage, like systemic inflammation and nutritional deficiencies. Healing your gut can also help to mitigate lingering symptoms of gluten, like gluten diarrhea. Below are some ways to help promote healing. For more support and comprehensive information, check out our
Glutenology© Masterclass
Incorporate nutrient-rich and gut-healing foods in the diet
Foods like bone broth can help to heal and repair the gut lining. Bone broth can also help to rehydrate your body. Your body may be less tolerant to certain foods as you begin to heal, but aim to eat whole unprocessed foods like grass-fed beef, pasture-raised poultry and eggs, and
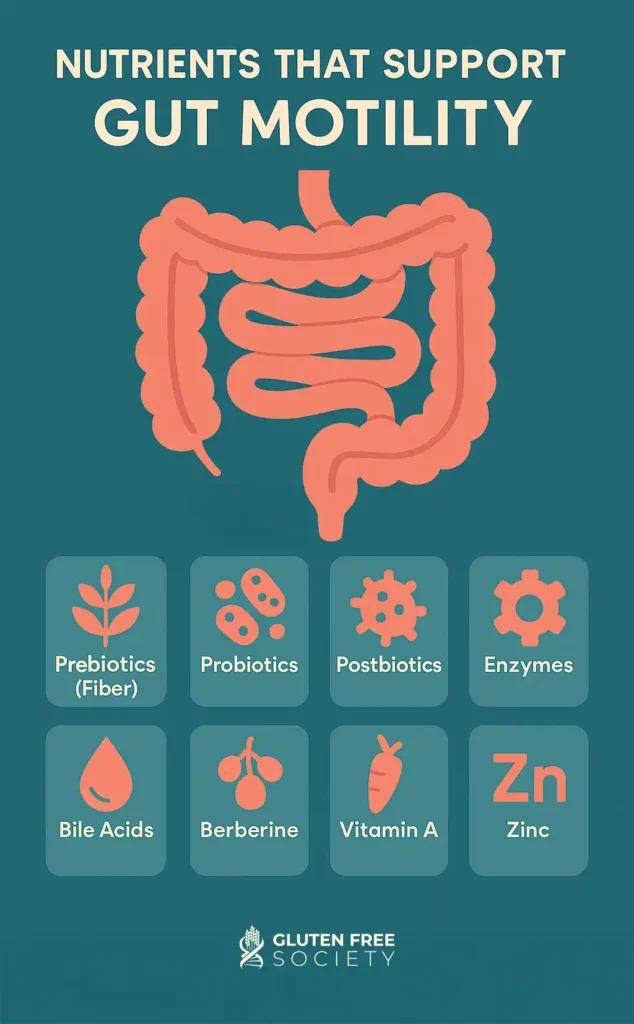
Promote gut health through probiotics, prebiotics, and postbiotics
Probiotics (good bacteria) and prebiotics (the food that feeds probiotics) can help to rebalance a dysbiotic or unbalanced gut, which is common in those who have been exposed to gluten. In particular,
research suggests that Saccharomyces boulardii may be the most effective probiotic for treating acute diarrhea in children. Many other
studies have linked probiotic supplementation to relief from diarrhea, and to better stools as measured by frequency and the Bristol Stool Chart.
Postbiotics contain inactivated microbial cells or cell components, so they are more stable than probiotics, but exert similar health benefits. For those who are sensitive to probiotics due to other underlying conditions, postbiotics may be beneficial.
Explore natural remedies to reduce inflammation and support healing
Foods and supplements like turmeric, ginger, and omega-3 fatty acids can help to manage inflammation as the body heals. In addition,
research suggests that berberine may be effective in shortening the duration of diarrhea. We share more on supplementation in the next section, and you can read our
Ultimate Guide To Supplements here.
Digestive Enzymes
A digestive enzyme is a complex protein made by the body that helps to break down food into smaller molecules. Breaking down food helps it to be more easily and completely absorbed into your body. Your body produces its own digestive enzymes in the mouth, pancreas, stomach, and small intestine. However, for some people, production of digestive enzymes has slowed, and they benefit from supplemental enzymes.
Some research has suggested that digestive enzymes can help support digestive symptoms. For example, a small
study of 31 patients with IBS found that people who were GOS sensitive and who received a full dose enzyme treatment with alpha-galactosidase supplementation had a reduction in symptoms of IBS when taken with foods that were high GOS.
Research suggests that micronutrient deficiencies increase a child’s susceptibility to diarrhea, but
vitamin A and zinc supplementation have been shown to reduce the incidence and hasten recovery from acute diarrhea episodes. Other research notes that
diarrhea is both a sign and cause of zinc deficiency.
Accurate test results can help guide your decisions around food choice and supplementation.
Gluten free supplements
Not all supplements are created equal. Many supplements use poor nutrient forms that are not well absorbed. In addition, many supplements (yes, even many premium or practitioner grade supplements) are cross contaminated with gluten. Therefore, it is critical to find a reputable company that specializes in providing gluten free supplements and that is committed to testing its ingredients and final products for gluten. Below is a list of trusted certified gluten free supplements that can support your body through celiac disease, gluten sensitivity, and diarrhea.
- Prebiotics (Fiber)
- Ultra Fiber is a complete fiber supplement that contains a combination of fibers derived from whole seeds, fruits, vegetables and roots, designed to support the health of the microbiome.
- Probiotics
- Biotic defense with S. boulardii: Biotic Defense with S. Boulardii is a unique probiotic formula designed to deliver active organisms shown to promote healthy gut microflora, protect intestinal integrity, and boost immune function. Included in this formula is Saccharomyces boulardii, an extensively researched microorganism shown to help reduce symptoms of diarrhea and restore microflora balance by enhancing commensal organism function
- Biotic Force: A probiotic formulated with an innovative prebiotic developed to support the growth of healthy bacteria in the gut through a method that is not fiber or starch-based so it does not promote flatulence in sensitive individuals.
- Postbiotics
- Ultra Butyrate: Butyrate is the primary fuel source for the cells of the large intestine, and it has been shown to play important roles in maintaining the gut barrier, modulating inflammation, and aids in proper gut motility. This “post-biotic” can be especially beneficial for individuals dealing with less than ideal gastrointestinal function.
- Enzymes
- Gluten Shield: Gluten Shield is an enzyme blend with probiotics designed to help maintain optimum digestion of all foods with a special focus on encouraging more complete digestion of complex carbohydrates in grains seeds, legumes, vegetables, and other plant materials. This digestive enzyme supplement is designed to help reduce the symptoms of occasional bloating, diarrhea, gas, and abdominal cramps associated with diets high in complex carbohydrates.
- Bile acids
- Lipogest: This product is designed to provide nutritional support for the liver and gallbladder. The liver is responsible for detoxification, protein and fatty acid synthesis, blood sugar regulation, hormone balance and healthy digestion. Because the liver supports almost every other organ and tissue system in the body, healthy liver function is essential for optimal vitality and wellbeing. One of the key processes of the liver is the production and excretion of bile, a substance that helps break down fats for digestion. Supporting the liver through this process can support optimal digestion and elimination.
- Berberine
- Ultra Berberine can support healthy microbial activity in the GI tract and may help promote GI Mucous membrane health.
- Vitamin A
- Ultra A: Ultra A supplies a concentrated source of Vitamin A in an emulsified form. For those struggling with celiac or gluten sensitivity, the gut does not always absorb vitamins effectively. Emulsification is used to assist with uptake and assimilation.
- Zinc
- Ultra Zinc is a complete formula that uses a blend of two fully soluble, ionized zinc sources. It was created for maximum absorption and effectiveness.
Diagnosing gluten sensitivity/intolerance
We understand that navigating the complexities of a gluten free lifestyle can feel overwhelming, so we at Gluten Free Society share a wealth of free information that includes the latest research, helpful tips and recipes, and answers to the questions that so many people have when on the gluten free journey.
For more information on testing and diagnosis,
read this article. And if you are uncertain if you have celiac disease, take our
gluten sensitivity quiz!
Conclusion
The journey to heal your gut and resolve your gluten diarrhea might feel daunting, but Gluten Free Society is here to walk you through it every step of the way. The effort will be well worth it to enjoy better health!


